Ignition Database Table Reference
Ignition has a lot of systems built-in that will query the database automatically without requiring you to build a query. These systems automatically create the necessary tables in the database, insert the relevant data, and even query it back out for you. However, because this data is all stored in simple database tables, it can be manually accessed using queries to customize how you see the data.
These tables are configured in very specific ways. Altering them may cause unforeseen issues, and is not recommended.
While it can be useful to manually query out data from these tables, we recommend taking a backup of the database tables before making changes, with the understanding that altering the data or tables is done at your own risk.
Tag History
The Tag History system utilizes at least six different tables in the database:
| Table Name | Table Description | Column References |
|---|---|---|
| sqlt_data_X_X | This table stores the raw tag data. There will be multiple tables that fit this format depending on the name of the Gateway and the date. (For example, a table named "sqlt_data_1_2018_01" would store data from the driver with an id of 1, for the year 2018, for the month of January) | sqlt_data_x_x_x.tagid = sqlth_te.id |
| sqlth_1_data | This table stores raw tag data, and is only used when the provider is configured to use a single partition (The provider's "Enable Partitioning" setting is unchecked). | sqlt_1_data.tagid = sqlth_te.id |
| sqlth_te | This table stores the non-data details of each tag. | sqlth_te.scid = sqlth_scinfo.id |
| sqlth_scinfo | This table stores tag group information. | sqlth_scinfo.drvid = sqlth_drv.id |
| sqlth_sce | This table stores start and end times for tag groups. | sqlth_sce.scid = sqlth_scinfo.id |
| sqlth_partitions | This table stores start and end times for each sqlt_data table. | sqlth_partitions.drvid = sqlth_drv.id |
| sqlth_drv | This table stores information about the drivers of the historical data. | none |
| sqlth_annotations | This table stores annotations for the Tag History system, such as those created by the Power Chart. | none |
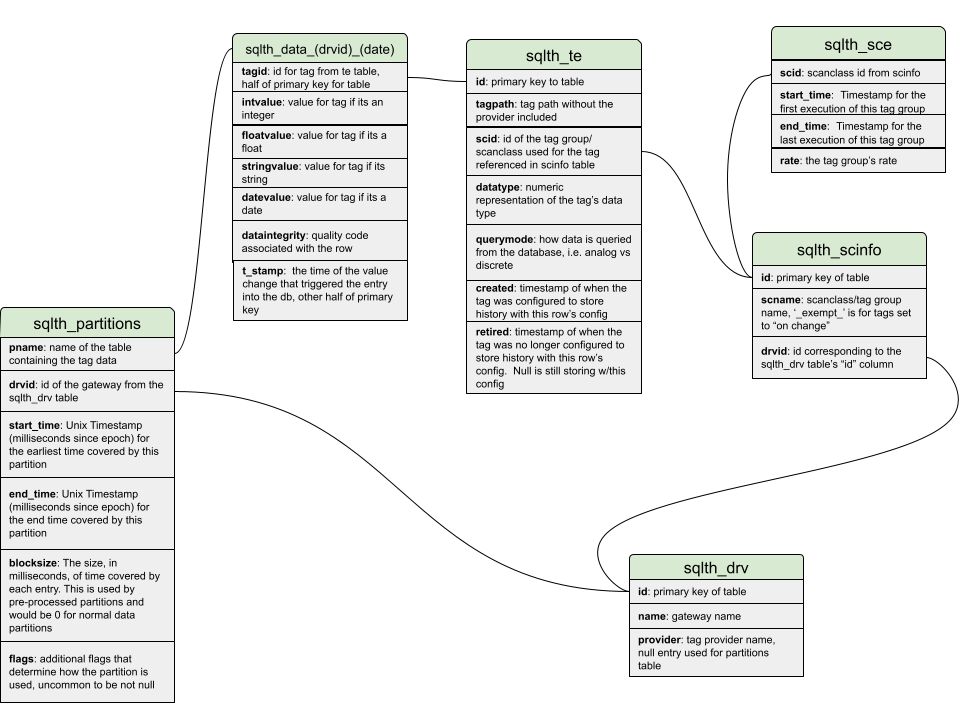
sqlt_data_X_X
This is the central table that stores the core tag values. The system stores data in tables based on the history provider's partition length and units. For example, a monthly partition would use a table named like sqlt\_data\_{driverId}\_{year}\_{month}, whereas a daily partition would use sqlt\_data\_{driverId}\_{yearMonthDay}. The duration of each partition is also tracked on the sqlth_partitions table.
When pre-processed partitions are enabled, an additional sql_data table will be created for each partition. The system tracks which partitions are pre-processed by the "blocksize" column on the sqlth_partitions table.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| tagid | int | Unique id of the tag. References the sqlth_te table. |
| intvalue | int | Stores the tag's value if it is type 0 (int/byte/short/boolean), otherwise NULL. |
| floatvalue | double | Stores the tag's value if it is type 1 (float/double/long), otherwise NULL. |
| stringvalue | string | Stores the tag's value if it is type 2 (string), otherwise NULL. |
| datevalue | date | Stores the tag's value if it is type 3 (DateTime), otherwise NULL. |
| dataintegrity | int | Quality of the tag at this timestamp. 192 = Good Quality. Other values represent uncertainty or bad quality. See Tag Quality Overlays. |
| t_stamp | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) for the record. |
| vtype | int | Represents metadata about the record, primarily used for pre-processed partitions. Possible flags include:
|
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- t_stamp
sqlth_1_data
This table stores raw tag data for history providers that have disabled partitioning (i.e., the Enable Partitioning setting is unchecked on the history provider). In this mode, data is stored in a single table named sqlth_1_data, instead of being split into multiple sqlt_data_X_X partitions.
The structure of this table is functionally identical to the sqlt_data_X_X tables, but without any partitioning logic.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| tagid | int | Unique ID of the tag. References the sqlth_te table. |
| intvalue | int | Stores the tag's value if it is type 0 (int/byte/short/boolean), otherwise NULL. |
| floatvalue | double | Stores the tag's value if it is type 1 (float/double/long), otherwise NULL. |
| stringvalue | string | Stores the tag's value if it is type 2 (string), otherwise NULL. |
| datevalue | date | Stores the tag's value if it is type 3 (DateTime), otherwise NULL. |
| dataintegrity | int | Quality of the tag at this timestamp. 192 = Good Quality. Any other value is considered poor quality or uncertain. See Tag Quality Overlays. |
| t_stamp | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) when the value was recorded. |
| vtype | int | Represents metadata about the record. This value is used with pre-processed partitions. Possible flags include:
|
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- t_stamp
sqlth_te
This table stores metadata for each historical tag. A row in this table represents a unique version of a tag's historical configuration. When a tag is modified in certain ways (renamed, data type changed, etc.), a new row is inserted and the previous entry is "retired."
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID of the tag. Primary key for this table. |
| tagpath | string | Full path of the tag within the Tag Provider, e.g., Folder1/tag1. |
| scid | int | Scan class (Tag Group) ID. References the sqlth_scinfo table, indicating the scan class this tag uses. |
| datatype | int | Determines which column in the partition tables stores the tag’s historical value.
|
| querymode | int | Reflects the Deadband Style setting selected when tag history was enabled.
|
| created | long | Unix timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) for when this tag entry was created. |
| retired | long | Unix timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) for when this tag entry was retired. NULL means the entry is currently active. A tag is marked as retired when any of the following occur:
|
Default indexing includes:
- id
- scid
sqlth_scinfo
This table stores information about Tag Groups (historically called scan classes). Each group defines how frequently a set of tags should record data. Tag Groups are also tied to a specific history driver. See sqlth_drv.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID of the Tag Group. |
| scname | string | Name of the Tag Group. A value of "exempt" is used when the execution rate is not recorded. |
| drvid | int | Driver ID this Tag Group belongs to. References the sqlth_drv table. Used to separate data when multiple Gateways or providers write to the same database. |
Default indexing includes:
- id
- drvid
sqlth_sce
This table tracks execution periods for each Tag Group over time. Each row marks a continuous span during which a Tag Group (i.e., scan class) was actively executing at a specific rate. This is useful for understanding when and how often tags within a group were scheduled to record data.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| scid | int | References the sqlth_scinfo table. Identifies which Tag Group this execution period belongs to. |
| start_time | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) representing the start of the execution period. |
| end_time | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) representing the end of the execution period. |
| rate | int | Execution rate in milliseconds for this Tag Group during the time window defined by start_time and end_time. This value is omitted for tags using On Change scan mode. |
Default indexing includes:
- scid
- start_time
sqlth_partitions
This table defines the data partitions used by the Tag Historian. Each row maps a time range to a specific table (usually a sqlt_data_X_X table), allowing for efficient querying across large datasets. Partitioning is key for scaling history storage over time, and the system consults this table to determine where to look for historical values.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| pname | string | The name of the table that stores data for this partition, e.g., sqlt_data_1_2025_04. |
| drvid | int | The driver that owns this data table. References the sqlth_drv table. Partitions are created per driver to keep records distinct. |
| start_time | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) marking the beginning of the time window covered by this partition. |
| end_time | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) marking the end of the time window for this partition. |
| blocksize | int | The duration (in milliseconds) of each block of pre-processed data in the table. A value of 0 means this is a regular data partition. |
| flags | int | Additional flags that affect how the partition is used. 1 = No seed query support. The system will not attempt bounding value ("seed") queries on this partition, which can improve performance on databases with limited indexing. |
Default indexing includes:
- pname
- start_time
sqlth_drv
This table stores information about drivers, which represent the source systems writing Tag History data. Each driver typically corresponds to an Ignition Gateway or Tag Provider. This distinction is important when multiple Gateways write to the same database, or when a Gateway has multiple Tag Providers enabled.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for the driver. Used by other tables (like sqlth_partitions and sqlth_scinfo) to associate partitions and Tag Groups with a specific driver. |
| name | string | System name of the Ignition Gateway that originated the data. When multiple Gateways are configured to write to the same historical database, this identifies where each record came from. |
| provider | string | Name of the Tag Provider within the Gateway. Useful when the same Gateway hosts multiple providers and stores data for each one. |
Default indexing includes:
- id
sqlth_annotations
This table stores annotations, user-created notes or metadata, tied to specific points or time ranges in Tag History. These annotations can be added through tools like the Perspective Power Chart or via scripting. They are useful for marking maintenance windows, process events, or any custom context.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID of the annotation. |
| tagid | int | The ID of the ag this annotation applies to. References the sqlth_te table. |
| start_time | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) marking the beginning of the annotation's time range. |
| end_time | long | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) marking the end of the annotation's time range. |
| type | string | Type of annotation. Currently, the only supported type is "note", which represents user-entered text. |
| datavalue | string | The content of the annotation (e.g., the user’s note text). Only applicable when type is "note". |
| annotationid | string | New in 8.1.4 A UUID used to track annotations. This identifier is used to track similar annotations across multiple Gateways, such as when storing annotations in a remote provider. |
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- start_time
Tag History - Internal History Provider
Internal History Providers use a different table scheme compared to external providers. These tables are stored in an IDB file located at IgnitionInstallationDirectory/data/local/tag-historian.
You’ll need a SQLite viewer to explore this data manually, since the system handles it outside of the configured database connections.
| Table Name | Table Description |
|---|---|
| annotations | Stores annotations for specific tags, including notes created via components like Power Chart. |
| schema_info | Tracks the schema version and creation timestamp of the internal historian. Usually contains one row. |
| tagdata | Holds the actual recorded values, timestamps, and quality codes for each tag. |
| tagdetails | Tracks tag metadata such as datatype and time-to-live settings. Does not include scan class/group info. |
| tagproperties | Stores individual tag properties like interpolation mode, deadband, and datatype. |
| tags | Maps each tag’s ID to its full tag path, allowing for efficient querying. |
annotations
These entries mirror those in sqlth_annotations, but are specific to local history and internal data storage.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID of the annotation. |
| tagid | int | The ID of the ag this annotation is associated with. Maps to the id column in the tags table. |
| type | text | Annotation type. Typically "note" for user-created textual annotations. |
| rangestart | int | Start time of the annotation (Unix Timestamp, in milliseconds since epoch). |
| rangeend | int | End time of the annotation. |
| data | text | The annotation content (e.g., text of the user note). |
| syncid | int | Identifier used to synchronize annotations across multiple Gateways. |
| annotationid | int | A UUID that uniquely identifies the annotation. Enables tracking across systems. |
| deleted | boolean | Marks whether the annotation has been logically deleted. Used to hide rather than remove data. |
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- rangestart
schema_info
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| version | int | Indicates the schema version used by the internal historian. Typically set to 4. |
| created | int | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) representing when the internal historian was first initialized. |
Default indexing includes:
- version
tagdata
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| tagid | int | References the tag's ID from the tags table. Identifies which tag this record belongs to. |
| numvalue | numeric | The numeric value of the tag at this time, if applicable. Will be NULL if the value is non-numeric. |
| strvalue | text | The string value of the tag at this time, if applicable. Will be NULL if the value is numeric. |
| quality | int | Quality code associated with the Tag value. See Tag Quality Overlays. |
| t_stamp | int | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) representing when the value was recorded. |
| syncid | int | ID used to track and synchronize records across Gateways. |
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- t_stamp
tagdetails
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique identifier for this metadata entry. |
| tagid | int | References the tag ID from the tags table. Associates this detail row with a specific tag. |
| created | int | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) for when this detail row was created. Marks the start of history storage for this version of the tag. |
| retired | int | Unix Timestamp (milliseconds since epoch) for when this detail row was retired. A value of NULL means it's still active. |
| datatype | int | Integer representing the stored data type:
|
| ttl | int | Time-to-live, in milliseconds. If non-zero, represents how long the data is retained before eligible for pruning. |
| syncid | int | Sync ID used to track and coordinate this record across multiple Gateways. |
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- created
tagproperties
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| tagid | int | References the tag ID from the tags table. Each property row is linked to a specific tag. |
| name | text | The name of the property. Common values include:
|
| value | text | The property's stored value, as a string. Interpreted based on the name property. |
| datatype | int | Integer representation of the property's data type. Uses the same encoding as sqlth_te.datatype:
|
Default indexing includes:
- tagid
- name
tags
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique identifier for the tag. This value is referenced by other internal historian tables. |
| tagpath | text | Full path of the tag, including its Tag Provider. For example: [default]Folder1/MyTag. |
Default indexing includes:
- id
- tagpath
Alarm Journal
The Alarm Journal system stores a record of all alarm events—activations, clearings, acknowledgments—along with event-specific data.
By default, it uses two database tables, though the table names can be customized in the Alarm Journal profile settings.
| Table Name | Table Description | Column References |
|---|---|---|
| alarm_events | Stores a row for each alarm event (active, cleared, acknowledged). | alarm_events.id = alarm_events_data.id |
| alarm_events_data | Stores name-value pairs of metadata for each event. Multiple rows may exist per event. | none |
alarm_events
This table captures the main record of each alarm event that occurred. One row is created for each change in state (active, cleared, acknowledged).
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for this event. Primary key. |
| eventid | int | Identifier that groups related event records together. All active, cleared, and acknowledged states for a single alarm occurrence share the same eventid. |
| source | string | The source path of the alarm, such as a tag path or expression item. |
| displayPath | string | Human-readable display path of the alarm (can be overridden in alarm configuration). |
| priority | int | Alarm priority level:
|
| eventtype | int | Alarm state change:
|
| eventflags | int | Bitmask representing metadata about the event (e.g., whether it was system-generated). |
| eventtime | datetime | Timestamp for when the event occurred. |
Default indexing includes:
- id
alarm_events_data
This table stores event-specific properties, such as custom alarm properties or tag values at the time of the event. Each row represents one property for one event.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | References the id from the alarm_events table. |
| propname | string | Name of the property (e.g., "AckUser", "Notes", or "IsShelved"). |
| dtype | int | Represents the type of value stored in this row:
|
| intvalue | int | Value of the property if dtype = 0. Otherwise NULL. |
| floatvalue | float | Value of the property if dtype = 1. Otherwise NULL. |
| strvalue | string | Value of the property if dtype = 2. Otherwise NULL. |
Default indexing includes:
- id
Authentication
The Database Authentication system allows you to manage users, roles, and authentication-related data using a SQL database.
By default, it uses six tables to represent user information. You can customize the table prefix (e.g., from scada_ to something else) in the Gateway settings.
| Table Name | Table Description | Column References |
|---|---|---|
| scada_users | Stores user credentials and basic profile data. Each row represents a user. | none |
| scada_roles | Stores defined roles. Each row is a distinct role. | none |
| scada_user_rl | Maps users to their assigned roles. Users with multiple roles will have multiple rows here. | scada_user_rl.user_id = scada_users.idscada_user_rl.role_id = scada_roles.id |
| scada_user_sa | Tracks upcoming schedule adjustments for users. Each adjustment gets its own row. | scada_user_sa.user_id = scada_users.id |
| scada_user_ci | Stores contact information for users, such as phone numbers and emails. Each entry is one piece of contact info. | scada_user_ci.user_id = scada_users.id |
| scada_user_ex | Stores additional user properties (used by modules like Voice Notification). Each property is a name/value pair. | scada_user_ex.user_id = scada_users.id |
scada_users
This is the core user table. It contains authentication credentials and general profile information for each user.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for the user. |
| username | string | The user's login name. |
| password | string | Encrypted password hash. |
| firstname | string | User’s first name. |
| lastname | string | User’s last name. |
| schedule | string | Assigned schedule name (for On-Call Roster or Scheduled Roster logic). |
| notes | string | Optional user notes. |
Default indexing includes:
- id
scada_roles
Stores all defined roles that can be assigned to users.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for the role. |
| name | string | Name of the role (e.g., "Administrator", "Operator"). |
Default indexing includes:
- id
scada_user_rl
Links users to their assigned roles. One row per user-role pair.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| user_id | int | References scada_users.id. |
| role_id | int | References scada_roles.id. |
Default indexing includes:
- user_id
- role_id
scada_user_sa
Stores schedule overrides or adjustments for individual users.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for the schedule adjustment. |
| user_id | int | References scada_users.id. |
| starttime | datetime | When the schedule adjustment starts. |
| endtime | datetime | When the schedule adjustment ends. |
| type | string | Type of adjustment (e.g., "Available", "Unavailable"). |
Default indexing includes:
- user_id
scada_user_ci
Stores pieces of contact info for users, such as emails or phone numbers.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for the contact info entry. |
| user_id | int | References scada_users.id. |
| type | string | Type of contact (e.g., "Email", "Phone"). |
| value | string | Contact information value. |
Default indexing includes:
- user_id
scada_user_ex
Stores custom or extra properties for a user. Often used by modules (e.g., Voice Notification) to store settings like PIN codes.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | Unique ID for the property. |
| user_id | int | References scada_users.id. |
| name | string | Name of the property (e.g., "VoicePIN"). |
| value | string | Value of the property. |
Default indexing includes:
- user_id
Audit Log
The Audit Log system tracks project and system activity for audit-enabled projects. Events like tag edits, script runs, user logins, and more are logged to a database.
By default, the Audit Log uses a single table—though you can rename it in the Gateway’s Audit Profile settings.
| Table Name | Table Description | Column Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AUDIT_EVENTS | Stores every auditable event that occurred, such as edits, tag writes, user logins, saves, publishes, and more. | none |
AUDIT_EVENTS
This table stores each individual auditable event. A new row is created for every logged action across Gateway, Designer, or Client scopes.
| Column Name | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AUDIT_EVENTS_ID | int | Unique identifier for the event. Primary key. |
| EVENT_TIMESTAMP | datetime | Timestamp for when the action occurred. |
| ACTOR | string | The user or system that performed the action. |
| ACTOR_HOST | string | Hostname or IP of the system where the action originated. |
| ACTION | string | Brief description of the action (e.g., "Tag Write", "Script Run"). |
| ACTION_TARGET | string | The target affected by the action (e.g., tag path, script name, user). |
| ACTION_VALUE | string | The value involved in the action (e.g., written value, changed property). |
| STATUS_CODE | int | A 32-bit integer bitmask representing the result of the action (e.g., good, bad, uncertain). Refer to AuditStatus.SubCode for decoding specific status codes. |
| ORIGINATING_SYSTEM | string | Name of the project or system that performed the action. |
| ORIGINATING_CONTEXT | int | Numeric bitmask representing the context of origin:
|
Default indexing includes:
- audit_events_id
- event_timestamp