Kafka
💡Have feedback for this page? Let us know on the IA Forum.
Kafka is a distributed event streaming system that allows you to process data in real time. The Kafka platform works by having producers create and publish events (also called records or messages) to a topic. Topics can be broken down into partitions, both of which are inside a server called a broker.
Events within topics are consumed by consumers, which use an offset to track which events have already been processed. Consumers can be further organized into consumer groups, which consume records from a set of topics.
Within a consumer group, a single partition can only be consumed by one consumer. However, multiple consumers can consume the same partition if the consumers are from different groups.
Unlike many other services, Kafka operates on a pull-based system, making it much more scalable as Kafka consumers can pull and consume topic data at varying rates. Additionally, using a pull-based system allows consumers to receive data in more optimized batches, as the consumer itself will pull all available messages that have not yet been processed. This helps eliminate any latency or buffering issues that stem from a push system.
See the official Kafka documentation for more information on Kafka.
Module Information
The Kafka Cloud Connector comes bundled with Ignition Cloud Edition, but can also be used with a standard version of Ignition. Features of the Kafka Cloud Connector include:
- Connectivity to Kafka systems through the Gateway Webpage interface.
- Integration with Ignition Event Streams for data processing.
- System Functions to interact with connected Kafka systems.
Gateway Interface
Installing the Kafka Cloud Connector module will result in a new configurable form on the Gateway that allows you to create Kafka connections.
These connections connect to a Kafka cluster, which can then be used for event streams or Kafka system functions. To create a Kafka connection, navigate to the Gateway Webpage's Connections section > Service Connectors > Connections.
Although it's possible to connect to an individual broker, it is recommended to connect to multiple brokers for redundancy and to prevent data loss.
The tables below outline the properties available when creating or editing a Kafka connection.
Main Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of your Kafka connection. |
| Description | A description of your Kafka connection. |
| Enabled | Enable or disable the Kafka connection. Default is enabled. |
| Bootstrap Servers | A list of host and ports (host:port) used for establishing a connection to the Kafka cluster, such as localhost:9092. |
| SASL Mechanism | The SASL mechanism to use for client connections. This can be any mechanism for which a security provider is available. Default is GSSAPI. |
| Security Protocol | The security protocol used when communicating with brokers. Default is PLAINTEXT. Options include:
|
| Username | The username to use when connecting. This value will be injected into the sasl.jaas.config configuration property. |
| Password | The password to use when connecting. This value will be injected into the sasl.jaas.config configuration property. Options include None, Embedded, or Referenced. |
| Custom Client Properties | Any properties you want applied to producer and consumer clients, line separated by key value pairs. When entering multiple key value pairs, you must use the following format: Note: If you are using a custom keystore, you will need to define the path to the custom keystore here using the property ssl.truststore.location=<keystore_location>. |
TLS/SSL Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | The specific SSL version to be used for the selected Security Protocol. If PLAINTEXT is selected, this setting is ignored. |
| Key Password | The password for the private key. Options include None, Embedded, or Referenced. |
| Keystore Type | The keystore type for how client and server certificates are stored. |
| Keystore Password | The password for the keystore. Select None if no custom keystore is selected. |
| Keystore Key | The password for the keystore key. Select None if no custom keystore is selected. |
| Truststore Password | The password for the truststore. Select None if no custom truststore exists. |
Additional Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Consumer Properties | A dictionary of properties applied only to consumers, as key value pairs. This property will override any duplicate keys from the Custom Client Properties. If entering multiple key value pairs, you must use the following format:
|
| Custom Producer Properties | A dictionary of properties applied only to producers, as key value pairs. This property will override any duplicate keys from the Custom Client Properties. If entering multiple key value pairs, you must use the following format:
|
Connecting to a Kafka System
This section describes how to create a Kafka connection.
-
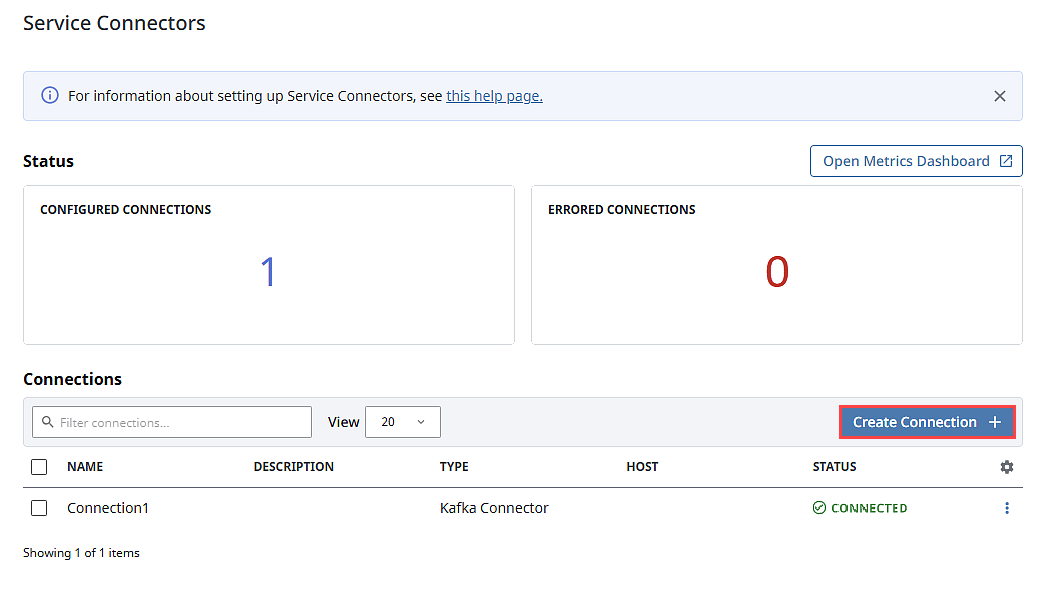
On the Gateway Webpage, navigate to Connections > Service Connectors > Connections.
-
Click Create Connection +.
-
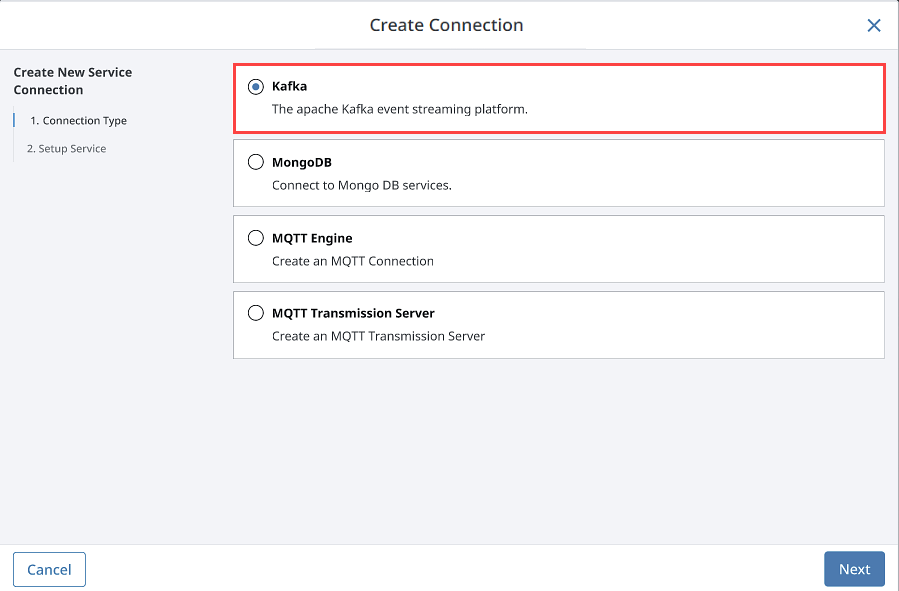
Select Kafka Connector. Click Next.
-
Fill out the Gateway fields with the appropriate information from your desired Kafka broker, then click Create Connection.
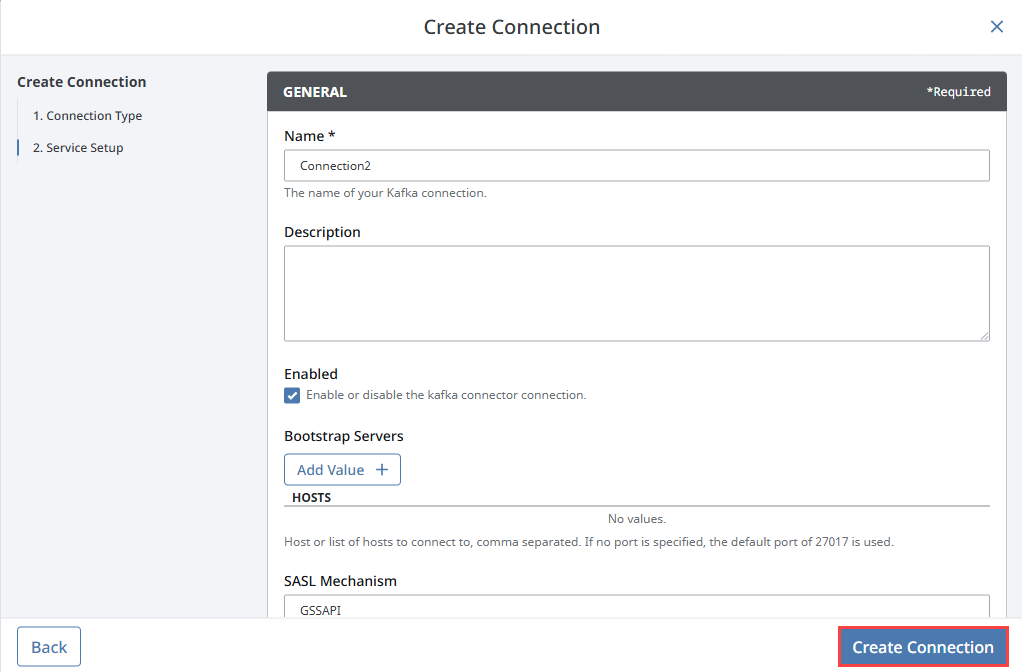
Your Kafka connection is now created. It may take a few seconds for your connection to update to a Valid status.
Using Kafka with Ignition Event Streams
The main way to interact with Kafka within the Ignition platform is through event streams. Event streams can use Kafka as both a source for receiving messages and a handler for sending messages to a Kafka topic. When using the Kafka event stream source, you can configure properties such as how to receive messages, where the message should come from, any consumer properties you want to invoke, and more. Similarly, when using the Kafka event stream handler, you can configure properties such as the topic to publish the message to, headers you want to include, any producer properties you want to invoke, and more. See the Event Streams page for more details.
Kafka System Functions
Many of Kafka's features are used within an event stream as either sources or handlers. The Kafka system functions allow similar capabilities if you need to utilize specific features of an event stream, such as polling or sending records. See the Kafka System Function page for a list of available system functions.